Electrohome Limited was a manufacturer of home electronics, appliances, furniture, and high-tech commercial projection and display systems, and an investor in television broadcasting, based in Kitchener. It once employed 4400 people in almost 1.6 million square feet of factories and service areas in Kitchener, Waterloo, and Cambridge, and sales offices throughout North America and Europe. It also established manufacturing facilities in the US and abroad.
In 1907, Arthur B. Pollock began manufacturing hornless phonographs in Berlin (now Kitchener), and together with Alex Welker established the Pollock Manufacturing Company in 1909. They soon acquired a woodworking plant in Elmira for the construction of phonograph cabinets and in 1917 formed the Phonola Company of Canada to continue the phonograph assembly and record business. The Pollock Manufacturing Company continued to produce parts for the phonographs and other metal products.
In 1925, the two business partners formed a new company, Pollock-Welker Limited. They also established the Grimes Radio Corporation to produce and sell Grimes radios in Canada. In 1933, Pollock combined his companies to form Dominion Electrohome Industries Limited. His son Carl became general manager of the new company, which was commonly called Electrohome. It had three manufacturing divisions: radio and communications, appliances and metal products, and furniture and woodworking.
Carl A. Pollock replaced his father as president in 1951 and brought about organizational change to manage the growing company; he oversaw the most successful years of Electrohome’s history. During the decades to follow, Electrohome produced many different consumer products, including:
Furniture: The name Deilcraft (from the first four letters of the company’s name) was introduced around 1937 and became a household name in the Canadian home furnishings industry. This division grew from the original 30,000 sq. ft. cabinetry plant in Elmira with 50 employees to the 400,000 sq. ft. woodworking plant built in a Kitchener industrial park in 1965 – Canada’s largest cabinet plant. In addition to television and stereo cabinets, the Deilcraft division produced bedroom and dining room sets and occasional furniture.
Electric motors: Electrohome was the largest producer in Canada of sub-fractional horsepower DC and AC motors, manufacturing more than 400 models at the rate of 10,000 a day by the 1960s. The 10 millionth small electric motor was made at the Victoria Street plant in 1967. The motors were used in many Electrohome products as well as appliances by other manufacturers.
Small appliances: Humidifiers, air conditioners, heaters, and other ‘home comfort’ products formed a significant part of the company’s production starting in the 1930s. Electrohome also became the largest manufacture of fans in Canada. The company produced many other small appliances over the years, from air purifiers to electric mixers and electric bug killers to microwaves.
Stereo and television: The company manufactured radios from the beginning, and the 1940s saw developments in television receivers. By the early 1950s, Electrohome was producing many models of each as well as radio-TV-phonograph combinations. Their sound quality was enhanced with the development of high-fidelity and then stereophonic sound. In 1965 the first colour-television sets became widely available and in 1969, colour television was the company’s largest single product line. In fact, Electrohome engineered and designed the only Canadian colour television receiver. The post-war population explosion had created a boom in housing construction and as a result the demand for consumer products like stereo hi-fi and television steadily increased. Countless Canadian living rooms had an Electrohome television or stereo console.
By 1965, Electrohome products were being sold in 23 countries. Total sales in 1968 were $44.5 million. By end of the decade, Electrohome was the second largest employer in Kitchener-Waterloo (behind the Dominion Rubber Company).
In 1972, Carl’s son John A. Pollock became president of the company, now officially called Electrohome Limited. The next decade saw many changes for the company, some of them influenced by increasing competition and imports in the television market and an economic recession.
Electrohome abandoned television manufacturing and the electronics division focused on commercial and industrial products, including specialized video and data display monitors and large-screen projection television. It also entered new fields, including reverse osmosis/ultrafiltration systems and monitors for coin-operated video games: Electrohome supplied custom-made monitors for many leading games manufacturers, including Atari and Sega, in the late 1970s and early 1980s. The company also had brief ventures in satellite television receivers and videotex hardware.
By the end of the 1980s, the company had stopped manufacturing consumer products altogether to focus on commercial data and video projection and display systems. In 1987 when Electrohome introduced the ECP 1000 single lens colour data and graphics video projector, the first of its kind in the world, the company was on its way to becoming a leader in this field. The Display Systems business focused on monochrome and colour monitors and high-performance LCD monitors and became a leading supplier for medical imaging and financial trading rooms. The Projection Systems business produced large screen colour video projection systems for data and graphics with developments in LCD and DLP (digital light processing) technologies.
By the end of the 1990s, Electrohome had sold these businesses and in 2004 the last manufacturing plant and head office building on Wellington Street in Kitchener was sold to Christie Digital Systems, Inc. In 2007, Electrohome sold its trademarks and soon the corporation’s shares were cancelled and delisted. Electrohome maintains an office in the Wellington Street building and is in the process of dissolving.
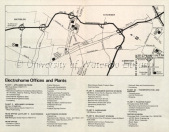
Electrohome plants over the years located in the Waterloo region include:
Plant 1: 283 Duke Street, Kitchener: cabinets, appliances
Plant 2: 480 Victoria Street, Kitchener: motor & metal products
Plant 3: 809 Wellington Street, Kitchener: head office, electronics, visual communications
Plant 4: 152 Shanley Street, Kitchener: furniture, appliances, warehousing
Plant 5: 140-144 Mansion Street, Kitchener: motors
Plant 6: Wilson Avenue and Fairway Road, Kitchener: cabinets, furniture, warehousing
Plant 7: Ottonabee Drive, Kitchener: plastics
Plant 9: Charles Street, Kitchener: furniture, warehousing
Plant 10: 505 Conestoga Boulevard, Cambridge: motors
Caya Building: 130 Weber Street, Kitchener: sales and administration
Pequegnat Building: 58-61 Frederick Street, Kitchener: technical products division
Electrohome also owned plants and acquired companies in Hawkesville, Stratford, Milverton, Wingham, Niagara-on-the-Lake, St. Catharines, Brantford, Nova Scotia, the US, and Malaysia.
Below: click to view a slideshow of more images from the archives of Electrohome.



















Thank you for making this slide show available, though I was hoping the show would include some images of the Clarion electronic organ sold by Electrohome.
. . . Jan Girardot
Historian, Musical Instrument Technicians Association, International
janandpat@sopris.net
I used to repair these Apollo stereos in Hamilton branch Electrohome Ltd., and was a road tech in the past up to 2004 owner Mike Collins, at the time previous manager of 809 Wellington St. service in Kitchener. I have acquired a few Electrohome radios, Viking etc., and a huge stereo console, Versailles, plus 1947 record am sw radio combo, Serenader, to remind me of the past 30 years with the company’s products. Thanks for the memories. I love this overview – it’s great, thanks!
Pingback: Communitech at 15: A parent’s (a.k.a. board chair’s) perspective
Thanks a lot for creating Electrohome | Doors Closed,
I just actually was researching for anything similar
and was glad to obtain the information by this
particular content.